History of Cars :
The modern car, therefore comes from a long list of venerated ancestors, and its lineage will, hopefully grow longer as we progress!
The birth of the car as we know it today occurred over a period of years. It was only in 1885 that the first real car rolled down on to the streets. The earlier attempts, though successful, were steam powered road-vehicles.
The first self-propelled car was built by Nicolas Cugnot in 1769 which could attain speeds of upto 6 kms/hour. In 1771 he again designed another steam-driven engine which ran so fast that it rammed into a wall, recording the world’s first accident.
 |
| Hydrogen Fuel Car (1807). |
In 1807 Francois Isaac de Rivaz designed the first internal combustion engine. This was subsequently used by him to develop the world’s first vehicle to run on such an engine, one that used a mixture of hydrogen and oxygen to generate energy.
 |
| Lenoir Gas-Engine Car (1862). |
This spawned the birth of a number of designs based on the internal combustion engine in the early nineteenth century with little or no degree of commercial success. In 1860 thereafter, Jean Joseph Etienne Lenoir built the first successful two-stroke gas driven engine. In 1862 he again built an experimental vehicle driven by his gas-engine, which ran at a speed of 3 kms/hour. These cars became popular and by 1865 could be frequently espied on the roads.
 |
| Damlier Four Stroke Engine (1885). |
The next major leap forward occurred in 1885 when the four stroke engine was devised. Gottileb Damlier and Nicolas Otto worked together on the mission till they fell apart. Daimler created his own engines which he used both for cars and for the first four wheel horseless carriage. In the meanwhile, unknown to them, Karl Benz, was in the process of creating his own advanced tri-cycle which proved to be the first true car. This car first saw the light of the day in 1886.
 |
| Ford T-Model (1908) |
The season of experiments continued across the seas in the United States where Henry Ford began work on a horseless carriage in 1890. He went several steps forward and in 1896, completed his first car, the Quadricycle in 1896. This was an automobile powered by a two cylinder gasoline engine. The Ford Motor Company was launched in 1903 and in 1908 he catapulted his vehicle, Model T Ford to the pinnacle of fame. Continuing with his innovations, he produced this model on a moving assembly line, thus introducing the modern mass production techniques of the automobile industry.
The modern car, therefore comes from a long list of venerated ancestors, and its lineage will, hopefully grow longer as we progress!
- How are new cars made?
First, they investigate what people want and what the current trends and fashions are.
Planning new cars starts three or four years in advance. Because of this, they have to decide what kinds of cars to make and set our goals and direction while thinking about what customers will want and how society will change in the future. We also have to determine what they think people’s lifestyles and preferences will be like in the future.
Designing :
When they finished investigating the car they prepare sketches of the car.They try to make the best possible car and check and revise the plans repeatedly.
 |
| Car Sketches. |
When they are done investigating the new car, they prepare sketches so they can see what it looks like.
They consider many different aspects of the design such as the outside shape and the inside shape and color. There are many things to decide about the interior, including the shape of the seats and meters, what materials they will use, and the layout of the different parts.
 |
| 3D Model & Clay Modeling. |
After ideas are narrowed down to a few sketches, computers are used to make three-dimensional images, and actual size clay models are made. A single idea is then chosen to be made into a beautiful design.
 |
| Designing. |
Once the design is decided, computers are used to create designs for the interior and exterior furnishings and the detailed parts. Designs are also created for the parts that provide the basic functions--driving, turning, and stopping--such as the engine and brakes.
Prototypes are made according to the design and many different tests are performed.
Testing :
Tests are done to find any weaknesses, the weaknesses are corrected, and the tests are performed again. This process is done over and over to develop better cars.
 |
| Collision Testing. |
The safety of vehicles is tested by colliding them to make sure that if a collision does occur the passengers .
 |
| High-Speed Driving Testing. |
Tests are conducted to make sure that the cars can drive safely on highways.
 |
| Rough Road Test. |
They imagine what roads around the world are like and perform tests to make sure cars can drive safely even .
 |
| Cross Wind Testing. |
We make sure that cars can drive safely even when there are strong crosswinds.
 |
| Break Testing. |
They make sure the brakes work properly.
 |
| Low-Temperature Testing. |
They check that cars will work properly even in cold regions.
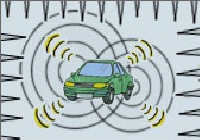 |
| Radio-Wave Effect Testing. |
Tests are conducted to make sure that radio waves don’t affect the computers and other devices used in cars.
 |
| Wet Road Testing. |
They perform tests to make sure cars can drive, turn, and stop safely even on wet roads.
 |
| Driving in Different Regions around the World. |
They conduct tests around the world according to road and climate differences in different regions.
Stamping :
The steel sheets used in the car bodies are sent from the steel-making company to the factory in big rolls.
 |
| Stamping . |
The steel sheet is cut according to the size of the part and then is bent and cut in a stamping machine to make parts such as car doors, roofs, and hoods. The stamped parts are inspected and then transported to the welding process.
Welding :







No comments:
Post a Comment